- Tel:+44 (0)1704 546 141
- Email:info@cofh.org.uk
The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones and 33 joints, including the ankle joint and the interphalangeal joints, found between the bones of the toes. The human foot is formed of more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments
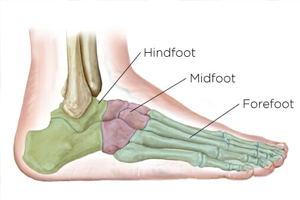
In medical descriptions the foot is often subdivided into the hindfoot, the midfoot, and the forefoot.
The hindfoot is the rear (posterior) part of the foot and starts below the ankle (talocrural) joint. The hindfoot contains the heel bone (calcaneus) and above it a saddle shaped bone (talus) that the weight-bearing shin bone (tibia) sits upon. It should be noted that the fibula bone of the lower leg on the outer (lateral) edge of the shin is not primarily weight-bearing and acts as an accessory bone to which muscles etc can be anchored.
The midfoot comprises five irregularly shaped bones (three cuneiform, the navicular and the cuboid) and usually contains the highest part of the inner arch of the foot. The foot has three arches, two of them lengthwise; the inner (medial) which can normally flex up and down acting in similar fashion to a cart-spring and helping to absorb the shocks from walking, the outer (lateral) arch which is usually relatively inflexible and the front (anterior) arch which runs from side to side across the forefoot.
The forefoot includes the five long bones (metatarsals) that come forward from the midfoot structure and join to the toes (phalanges). The big toe(hallux) has two bones (individually known as phalanx bones) one joined to the end of the first metatarsal (the proximal phalanx) and the next (the distal phalanx) joined to the far (distal) end of the proximal phalanx. The four remaining toes although normally smaller, have three individual phalanx bones (the proximal, intermediate and distal phalanx). The joints between the metatarsals and phalanges are called, unsurprisingly, the metatarsophalangeal joints (often abbreviated to MTP). They collectively form the anterior transverse arch mentioned previously. An enlarged 1st metatarsophalangeal joint is often called a ‘bunion’ (medically termed hallux-abductovalgus or HAV for short). A similar enlargement of the 5th MTP is sometimes called a ‘bunionette’ or ‘tailors bunion’, the latter term is claimed to reflect the facts that historically tailors squatted on the floor cross-legged while working and the pressure on the outer part of the foot irritated the 5th MTP and caused them to enlarge.
Covering the bony (skeletal) structure of the foot are the vast variety of muscles, ligaments and other tissue already mentioned. Tendons join muscles to bones and joints, ligaments hold joints together, other important tissues are fascia, which essentially acts as strapping to bind other groups of tissue together – usually in sheets or bands – and the padding tissue that is normally on the bottom of the foot to form cushioning (fibro-fatty padding).
Even from the very brief foregoing introduction to the foot it can be seen that such a complex part of the body (we did not even touch on the nerves and blood vessels!) requires its own specialist health professional to care for it.
Your Foot Health Practitioner can provide accurate and up-to-date footcare advice to help you to maintain foot health yourself and always stands ready to provide care and assistance in keeping your feet happy.